· 9 min read
AI-agenttien ja työnkulkujen rakentaminen Agent Frameworkin avulla
Transform complex business processes with multi-agent AI. Discover how to build scalable, automated workflows using the Microsoft Agent Framework

How Microsoft Agent Framework Enables Scalable Multi-Agent Workflows
This article is part of our 5-part series on AI Agent & Workflow Development Tools where we explore the leading platforms and frameworks for building production-ready AI solutions.
📚 Series: Tools We Use for AI Development
- Azure AI Foundry - How Azure AI Foundry helps you build secure enterprise AI solutions
- LangChain - How LangChain helps you build production-ready AI agents with Python
- Semantic Kernel - How Semantic Kernel helps you build multi-agent AI systems in .NET
- n8n - How n8n democratizes AI automation with low-code workflows
- Microsoft Agent Framework (this article) - How Microsoft Agent Framework enables scalable multi-agent workflows
What is the Microsoft Agent Framework?
The Microsoft Agent Framework represents a paradigm shift in how we build intelligent business automation. Released as part of Microsoft’s AI platform evolution, it’s a comprehensive development framework that enables developers to create, orchestrate, and manage autonomous AI agents that can work together to solve complex business problems.
Unlike traditional automation tools that follow rigid, pre-programmed paths, the Agent Framework empowers developers to build intelligent agents that can:
- Reason and Plan: Break down complex tasks into manageable steps and adjust strategies based on context
- Use Tools and APIs: Interact with databases, call external services, and execute functions to accomplish goals
- Collaborate with Other Agents: Work in teams where specialized agents handle different aspects of a workflow
- Learn from Context: Understand business context, user intent, and historical patterns to make informed decisions
- Handle Exceptions Gracefully: Adapt to unexpected situations without requiring explicit error handling for every scenario
At its core, the framework provides the building blocks for agentic AI - systems where AI doesn’t just respond to prompts but actively pursues goals, makes decisions, and takes actions autonomously within defined guardrails.
What’s New in the Microsoft Agent Framework
1. Native Multi-Agent Orchestration
The most groundbreaking innovation is built-in support for multi-agent collaboration:
- Agent-to-Agent Communication: Agents can request help from other agents, share context, and delegate subtasks
- Orchestration Patterns: Pre-built patterns for sequential workflows, parallel execution, hierarchical task decomposition, and event-driven collaboration
- State Management: Shared state and memory management across agent teams to maintain consistency
- Conflict Resolution: Intelligent handling of conflicting agent decisions with configurable resolution strategies
This eliminates the need to build custom orchestration logic, allowing developers to focus on defining agent capabilities and business logic.
2. Prompt Flow Integration
Seamless integration with Azure AI Studio’s Prompt Flow provides:
- Visual Agent Design: Drag-and-drop interface for designing agent workflows and decision trees
- Testing and Debugging: Built-in tools to test agent interactions, trace execution paths, and identify issues
- Version Control: Manage agent definitions and workflows with full version history
- Deployment Pipelines: One-click deployment from development to production environments
This makes agent development accessible to teams beyond just experienced developers, enabling citizen developers and business analysts to contribute to automation initiatives.
3. Enterprise-Grade Tool Ecosystem
The framework comes with a rich set of pre-built tools and connectors:
- Microsoft 365 Integration: Native access to Outlook, Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive, and other M365 services
- Business System Connectors: Pre-configured integrations with SAP, Salesforce, Dynamics 365, ServiceNow, and hundreds of other enterprise systems
- Data Access Tools: Query databases, call APIs, read files, and process structured/unstructured data
- Code Execution: Safely run Python, JavaScript, or SQL code for custom logic and calculations
- Custom Tool Framework: SDK for building and registering your own tools that agents can discover and use
Agents automatically discover available tools and determine which ones to use based on the task at hand.
4. Advanced Memory and Context Management
Sophisticated memory systems enable agents to maintain context across interactions:
- Short-Term Memory: Conversation history and immediate context for ongoing interactions
- Long-Term Memory: Persistent storage of facts, preferences, and learned patterns
- Semantic Memory: Vector-based storage for retrieving relevant information based on meaning, not just keywords
- Shared Memory Pools: Multiple agents can access common knowledge bases and working memory
- Memory Consolidation: Automatic summarization and organization of information to prevent context overflow
This allows agents to have “institutional knowledge” and maintain continuity across sessions, users, and time.
5. Safety and Governance Framework
Enterprise deployment requires robust safety mechanisms:
- Action Approval Workflows: Configure which actions require human approval before execution
- Guardrails and Constraints: Define boundaries for agent behavior, data access, and decision-making
- Audit Logging: Complete traceability of all agent actions, decisions, and interactions
- Content Moderation: Automatic filtering of inappropriate inputs and outputs
- Role-Based Permissions: Control which agents can access which tools and data sources
- Rollback Capabilities: Undo agent actions when mistakes are detected
These features ensure that autonomous agents operate safely within business policies and regulatory requirements.
6. Cost Optimization and Efficiency
Built-in mechanisms to optimize AI usage and costs:
- Intelligent Caching: Reuse results from previous similar queries to reduce API calls
- Model Selection: Automatically choose the most cost-effective model for each subtask
- Batch Processing: Group similar operations to reduce overhead
- Early Termination: Stop processing when sufficient information is gathered
- Resource Pooling: Share expensive resources like embeddings and knowledge bases across agents
Organizations can deploy sophisticated multi-agent systems without proportionally scaling costs.
How It Enables Custom Multi-Agent Business Workflows
Specialized Agent Roles
Instead of building one complex agent that tries to do everything, the framework encourages creating specialized agents:
Marketing Campaign Workflow:
├── Campaign Manager Agent (Orchestrator)
│ ├── Content Creator Agent
│ │ ├── Copywriting Sub-Agent
│ │ └── Image Generation Sub-Agent
│ ├── Audience Analyzer Agent
│ │ ├── Demographics Analyzer
│ │ └── Behavior Predictor
│ ├── Channel Optimizer Agent
│ │ ├── Email Campaign Agent
│ │ ├── Social Media Agent
│ │ └── Paid Ads Agent
│ └── Performance Monitor Agent
│ ├── Analytics Collector
│ └── ROI CalculatorEach agent has a focused responsibility, making the system easier to develop, test, maintain, and scale.
Dynamic Workflow Composition
Workflows aren’t rigid - agents can dynamically adapt their collaboration patterns:
Example: Customer Support Workflow
- Intake Agent receives customer inquiry
- Analyzes intent and routes to appropriate specialist:
- Technical issues → Technical Support Agent (can call Knowledge Base Agent or Engineering Agent)
- Billing questions → Billing Agent (can call Payment Processing Agent or Fraud Detection Agent)
- Product questions → Product Specialist Agent (can call Inventory Agent or Recommendation Agent)
- If unresolved, Escalation Agent determines appropriate human expert
- Follow-up Agent schedules check-in and ensures resolution
The workflow adapts based on the specific inquiry without requiring separate pre-programmed paths for every scenario.
Event-Driven Agent Collaboration
Agents can operate reactively based on business events:
Example: Order Fulfillment System
- Order Received Event → Order Processing Agent activates
- Validates order → calls Inventory Agent to check stock
- If low stock → Procurement Agent triggers reorder from supplier
- If high-value order → Fraud Detection Agent performs additional verification
- Shipping Agent coordinates with Logistics API for delivery
- Notification Agent sends updates to customer
- Analytics Agent records metrics for business intelligence
Each agent operates independently but coordinates through events and shared state, creating a resilient, scalable system.
Human-in-the-Loop Integration
Not all decisions should be fully automated. The framework supports hybrid workflows:
- Approval Gates: Agents pause and request human approval for critical actions
- Recommendation Mode: Agents suggest actions but let humans make final decisions
- Escalation Triggers: Automatically involve humans when confidence is low or stakes are high
- Learning from Feedback: Human corrections improve future agent behavior
This enables progressive automation - start with agents assisting humans, then gradually increase autonomy as trust and accuracy improve.
Real-World Multi-Agent Business Use Cases
1. Intelligent Document Processing Pipeline
Agents Involved:
- Document Ingestion Agent: Receives documents from email, SharePoint, or file uploads
- Classification Agent: Identifies document type (invoice, contract, resume, etc.)
- Extraction Agent: Pulls relevant data using specialized sub-agents for each document type
- Validation Agent: Checks extracted data for accuracy and completeness
- Routing Agent: Sends processed documents to appropriate business systems
- Exception Handler Agent: Flags issues for human review when confidence is low
Business Value: Process thousands of documents daily with 95%+ accuracy, reducing manual data entry by 80% while maintaining quality control.
2. Sales and Marketing Automation
Agents Involved:
- Lead Scoring Agent: Analyzes prospect behavior and assigns scores
- Content Personalization Agent: Creates customized messaging for each prospect
- Outreach Coordinator Agent: Determines optimal timing and channels for contact
- Engagement Monitor Agent: Tracks responses and adjusts strategy
- Qualification Agent: Determines sales-readiness and routes qualified leads
- Handoff Agent: Prepares comprehensive briefs for sales team
Business Value: Increase lead conversion rates by 40% while freeing sales teams to focus on high-value interactions.
3. Financial Operations Workflow
Agents Involved:
- Transaction Monitor Agent: Continuously watches for financial transactions
- Anomaly Detection Agent: Flags unusual patterns or potential fraud
- Compliance Check Agent: Ensures transactions meet regulatory requirements
- Reconciliation Agent: Matches transactions across systems
- Reporting Agent: Generates financial reports and dashboards
- Audit Trail Agent: Maintains complete documentation for compliance
Business Value: Reduce financial close time by 50%, catch fraud earlier, and ensure continuous compliance.
4. IT Operations and Incident Management
Agents Involved:
- Monitoring Agent: Tracks system health and performance metrics
- Incident Detection Agent: Identifies issues and categorizes severity
- Diagnostic Agent: Analyzes logs and traces to identify root causes
- Remediation Agent: Applies automated fixes for known issues
- Escalation Agent: Routes complex issues to appropriate teams
- Documentation Agent: Updates knowledge base with resolutions
Business Value: Reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR) by 60%, prevent 70% of incidents through proactive detection, and maintain comprehensive operational knowledge.
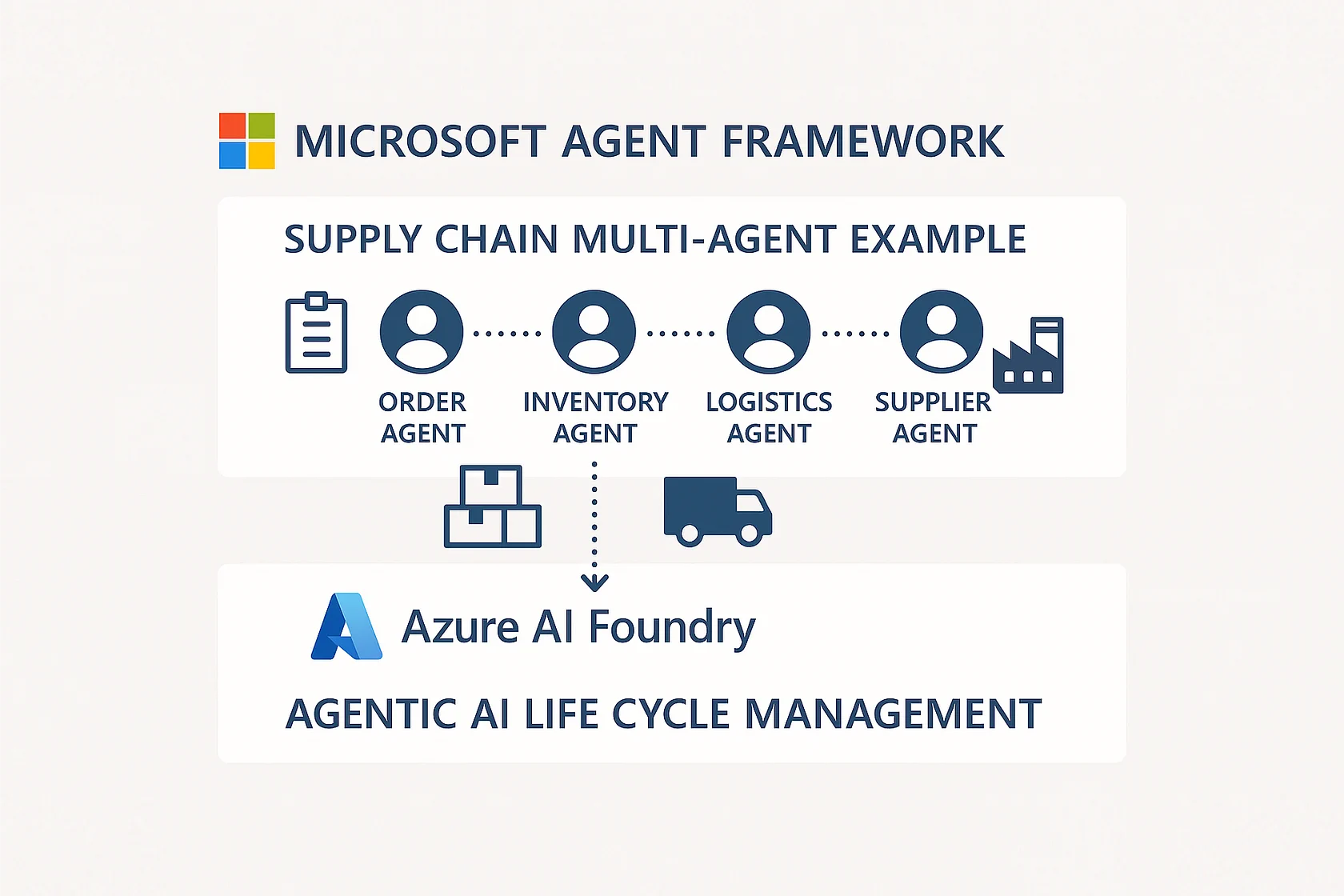
5. Supply Chain Optimization
Agents Involved:
- Demand Forecasting Agent: Predicts future product demand
- Inventory Management Agent: Optimizes stock levels across locations
- Procurement Agent: Manages supplier relationships and ordering
- Logistics Agent: Coordinates shipping and delivery
- Quality Assurance Agent: Monitors product quality and supplier performance
- Risk Management Agent: Identifies supply chain vulnerabilities
Business Value: Reduce inventory costs by 25%, improve delivery times by 30%, and minimize stockouts by 80%.
Building Your First Multi-Agent Workflow
The framework provides multiple entry points for different skill levels:
For Developers
from azure.ai.agents import Agent, Orchestrator, Tool
# Define specialized agents
data_analyst = Agent(
name="DataAnalyst",
model="gpt-4o",
instructions="Analyze data and provide insights",
tools=[query_database, create_visualization]
)
report_writer = Agent(
name="ReportWriter",
model="gpt-4o",
instructions="Create executive reports from analysis",
tools=[generate_document, format_charts]
)
# Create orchestrator
workflow = Orchestrator(
agents=[data_analyst, report_writer],
pattern="sequential"
)
# Execute workflow
result = workflow.run("Create quarterly sales report")For Low-Code Users
Use Prompt Flow visual designer to:
- Drag agent components onto canvas
- Connect agents with workflow lines
- Configure agent properties and tools
- Test with sample inputs
- Deploy to production
For Business Analysts
Define workflows in natural language:
- “When a support ticket is created, classify it, route to the appropriate specialist agent, and notify the customer”
- The framework translates this into an executable multi-agent workflow
Best Practices for Multi-Agent Systems
- Single Responsibility: Each agent should have one clear purpose
- Loose Coupling: Agents communicate through well-defined interfaces, not direct dependencies
- Graceful Degradation: System continues operating even if some agents fail
- Observable: Comprehensive logging and monitoring of agent interactions
- Testable: Each agent can be tested independently before integration
- Secure: Principle of least privilege - agents only access what they need
- Cost-Aware: Monitor and optimize token usage across agent teams
The Future of Business Automation
Microsoft’s Agent Framework represents the evolution from:
- Rules-based automation → Intelligent decision-making
- Single-purpose bots → Collaborative agent ecosystems
- Rigid workflows → Adaptive, context-aware processes
- Reactive systems → Proactive, goal-oriented agents
By enabling developers to orchestrate teams of specialized AI agents, businesses can tackle complex automation challenges that were previously impossible or impractical. The framework provides the infrastructure, safety mechanisms, and integration capabilities needed to bring agentic AI into production environments with confidence.
The Microsoft Agent Framework is not just about automating tasks - it’s about creating intelligent systems that can understand business context, collaborate to solve problems, and continuously improve over time. As AI capabilities advance, the framework ensures your automation investments grow more capable without requiring complete rebuilds, making it a future-proof foundation for enterprise AI initiatives.
Ready to Transform Your Business with AI?
Let's discuss how we can help you automate and optimize your workflows with cutting-edge AI solutions.
Book a free consultation